Braids
Interweaving of at least three yarns so that they intersect at an angle of 20° to 160°, in order to create a flat or tubular structure.
This process is widely used in the field of technical textiles because the resulting structure is very resistant to traction, while retaining an interesting flexibility.
Synthetic materials are mainly used for braiding, as they are continuous filaments with a smooth surface and high strength.

Basics patterns

Diamond

Regular

Hercules
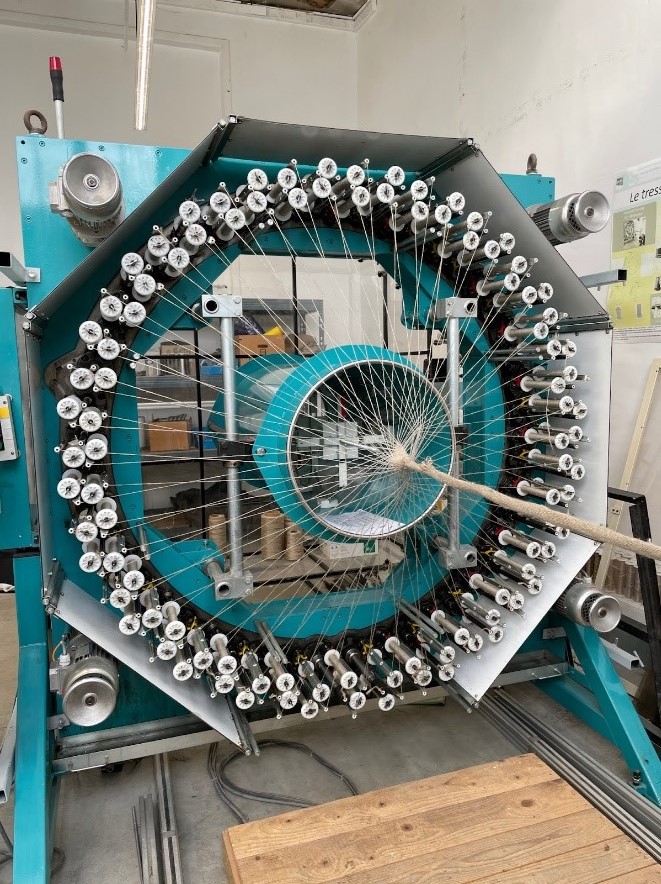
Braids processing
A braiding machine is used to form the braid. There are several possible configurations with one or more bobbin path (i.e. paths that the yarn follows).
It is possible to create rond braids, flat braids, as well as double braids (meaning that the circuit of formation of the braid can split in two then reform, which allows to obtain braidswith holes). Zero degree yarns can also be inserted to form triaxial braids. This type of insertion increases the strength of the braid.
Types of materials processed
Mainly organic synthetic material, we also find braids in natural plant material.
Characteristics
Breaking resistant, insulator, tends to create fibrils on fibrous materials (mainly vegetal).
Applications
Various ropes, ropes insulator, etc.


